感兴趣?立即联系我们
请填写右侧表单或直接通过以下邮箱与我们联系
sales@senecaesg.com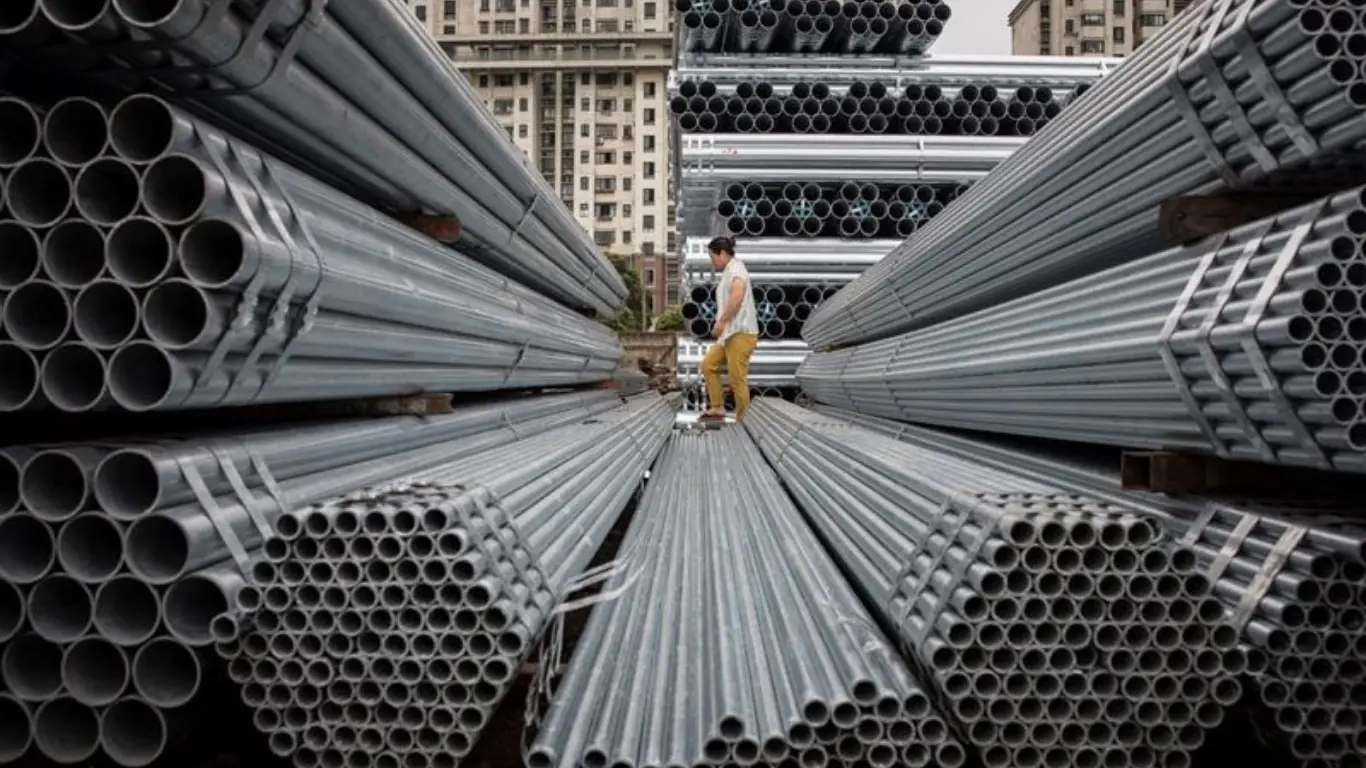
On July 22, 2025, researchers from the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) reported that China needs to reduce its steel output from coal-powered blast furnace processes by more than 90 million metric tons from 2024 levels to meet its green steel target for the year. The global steel industry is responsible for roughly 8% of global CO2 emissions, with China contributing to more than half of the world’s steel production. Achieving the target would significantly help China cut its carbon emissions.
According to the CREA analysts, if China succeeds in producing 15% of its steel from electric arc furnace (EAF) facilities this year, it could reduce CO2 emissions by more than 160 million tons—almost equivalent to the European Union’s steel sector emissions. However, China lags significantly behind other nations in adopting the electric arc furnace method, which is considered cleaner than the traditional blast furnace process. While the global average share of EAF steel production is around 30%, the U.S. leads with 71.8%, India at 58.8%, and Japan at 26.2%.
From 2021 to the first half of 2025, China’s blast furnace utilization increased from 85.6% to 88.6%, while electric arc furnace utilization dropped from 58.9% to 48.6%. This data indicates the growing reliance on the carbon-intensive methods. Belinda Schaepe, an analyst at CREA, emphasized that addressing China’s overcapacity in the steel sector, coupled with a shift to lower-emission production, could help solve structural issues within the industry while easing global trade tensions.
In 2024, China produced 1.005 billion tons of crude steel, with about 90% of it coming from blast furnace operations. The sector continues to grapple with overcapacity, contributing to low steel prices and sparking protectionist responses from international trade partners. The cleaner electric arc furnace method has faced challenges, including high energy costs, unstable scrap supply, and growing losses, which have hindered its widespread adoption.
Source:
监控投资组合中的ESG表现,创建自己的ESG框架,并做出更明智的商业决策。
请填写右侧表单或直接通过以下邮箱与我们联系
sales@senecaesg.com7 Straits View, Marina One East Tower, #05-01, Singapore 018936
+(65) 6223 8888
Carrer de la Tapineria, 10
Ciutat Vella, 08002, Barcelona, Spain
+34 612 22 79 06
77 Dunhua South Road, 7F Section 2, Da'an District Taipei City, Taiwan 106414
(+886) 02 2706 2108
Av. Santo Toribio 143,
San Isidro, Lima, Peru, 15073
(+51) 951 722 377