Interested? Contact us now
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com
The Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol is a comprehensive global standardized framework for measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions. Developed through a multi-stakeholder partnership of businesses, non-governmental organizations, governments, and others, the GHG Protocol provides essential guidelines for organizations to understand, quantify, and reduce their GHG emissions. Its significance is underscored by widespread adoption; in 2016, 92% of Fortune 500 companies responding to the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP) reported using the GHG Protocol directly or through a program based on its standards . This widespread use highlights the GHG Protocol’s critical role in helping organizations across the globe manage their environmental impact.
In this blog, we will provide a basic understanding of the seven main standards of the GHG Protocol, exploring their purposes and applications.
The GHG Protocol is a widely recognized and comprehensive framework for measuring and managing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Developed through a partnership between the World Resources Institute (WRI) and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), its purpose is to provide standards, guidance, tools, and training for businesses and governments to measure and manage their GHG emissions. The protocol covers a range of standards, including corporate, city, product, and value chain emissions, ensuring a holistic approach to GHG accounting.
Its popularity is underscored by its widespread adoption, with over 90% of Fortune 500 companies using it as reported by the CDP in recent years. The GHG Protocol continues to evolve, incorporating the latest scientific and policy developments to support effective climate action, reflecting its critical role in global sustainability efforts.
The Corporate Standard is the cornerstone of the GHG Protocol, designed to provide a standardized approach for companies to measure and manage their greenhouse gas emissions. Its primary purpose is to offer comprehensive guidelines that help organizations develop accurate, consistent, and transparent GHG inventories .
Purposes and Scopes
The Corporate Standard aims to assist companies in understanding their full GHG impact by covering emissions from all activities under their control. It encompasses three main scopes:
Main Content of the Standard
The Corporate Standard provides detailed guidance across key areas to ensure a robust GHG inventory for companies. It directs companies to define organizational boundaries by selecting operations under either the control or equity share approach. Operational boundaries are set by identifying emissions associated with specific activities categorized into Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3. Emphasis is placed on tracking emissions consistently over time to identify trends, set reduction targets, and measure progress effectively. The standard guides companies on collecting data, using emission factors, and accurately calculating GHG emissions. Best practices for transparently reporting emissions, including contextual information to support data credibility, are also outlined, promoting accountability and sustainability in corporate environmental management.
The Cities Standard, also known as the GHG Protocol for Cities, provides a comprehensive framework for cities to measure and manage their greenhouse gas emissions. This standard is crucial for urban areas, which are significant contributors to global GHG emissions due to high population densities and extensive industrial activities .
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Cities Standard is to enable cities to develop consistent and transparent GHG inventories, which are essential for creating effective climate action plans. The standard helps cities understand their emissions sources and identify opportunities for reductions.
The scope of the Cities Standard includes all emission sources within the city boundaries, organized into three main categories:
Main Content of the Standard
The Cities Standard offers detailed guidance on critical aspects to assist cities in developing accurate and comprehensive GHG inventories. It directs cities to define clear geographic and operational boundaries for their inventory, including sectors and sources to be included. The standard provides methods for identifying and categorizing emission sources across sectors like transportation, buildings, waste management, and industrial processes. Guidance on data collection, using emission factors, and applying methodologies ensures accurate emissions calculation and reliability. Cities are encouraged to track emissions consistently over time to monitor progress and evaluate climate policies’ effectiveness. Best practices for transparently reporting emissions data, including public disclosure and stakeholder engagement, are also emphasized to foster accountability and support sustainable urban development.
The Mitigation Goal Standard is a key component of the GHG Protocol, providing guidelines for governments, organizations, and other entities to design, implement, and track progress toward their greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction targets. This standard is crucial for ensuring that mitigation efforts are measurable, verifiable, and effective in reducing GHG emissions .
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Mitigation Goal Standard is to help entities set clear, achievable, and transparent GHG reduction goals and measure their progress over time. This involves creating robust frameworks for tracking emissions and evaluating the effectiveness of various mitigation strategies.
The scope of the Mitigation Goal Standard includes several types of mitigation goals, such as: Absolute reduction targets, Intensity targets, Baseline scenario targets.
Main Content of the Standard
The Mitigation Goal Standard offers detailed guidance on essential elements to ensure robust and credible GHG reduction goals. It directs entities on defining clear and ambitious mitigation goals, considering historical emissions, future projections, and relevant policies. The standard emphasizes the importance of clearly defining the scope, including GHGs, sectors, and geographic areas covered, for consistency and comparability. Guidance is provided on selecting an appropriate baseline year or scenario and methodologies for tracking emissions over time to monitor progress. Best practices for reporting progress transparently, including public disclosure, third-party verification, and stakeholder engagement, ensure accountability. This standard is indispensable for organizations committed to effective climate action and sustainability goals.
The Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Standard is an essential part of the GHG Protocol, providing guidelines for companies to measure and manage greenhouse gas emissions across their entire value chain. This standard is vital because Scope 3 emissions often represent the majority of a company’s total GHG impact, encompassing both upstream and downstream activities .
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Standard is to help companies comprehensively assess their indirect GHG emissions. By understanding these emissions, companies can identify significant reduction opportunities and improve their overall sustainability performance.
The scope of the standard includes 15 categories of Scope 3 emissions, such as: purchased goods and services, capital goods, fuel- and energy-related activities, upstream transportation and distribution, waste generated in operations, business Travel, employee commuting, downstream transportation and distribution, use of sold products, end-of-life treatment of sold roducts
Main Content of the Standard
The Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Standard offers clear and essential guidance in several critical areas. It directs companies on identifying Scope 3 emission sources throughout their value chain, ensuring a comprehensive assessment. The standard details methodologies for data collection and emission calculation across various Scope 3 categories, emphasizing accuracy with consistent emission factors. Companies are also instructed on defining inventory boundaries, deciding which categories and activities to include based on materiality and relevance. Best practices for tracking Scope 3 emissions over time and transparently reporting results, including public disclosure and stakeholder engagement, are also highlighted. This standard is pivotal for companies aiming to enhance sustainability by effectively managing and reducing their entire carbon footprint.
The Policy and Action Standard is a crucial framework within the GHG Protocol designed to help policymakers and organizations assess the greenhouse gas impacts of policies and actions. This standard is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of various climate initiatives and ensuring that they contribute meaningfully to emission reduction goals .
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Policy and Action Standard is to provide a consistent and transparent approach for estimating and reporting the GHG effects of policies and actions. This includes both planned and implemented initiatives, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions based on robust data.
The scope of the standard covers a wide range of policy types and actions, such as: Regulatory policies, Economic instruments, Subsidies and incentives, Voluntary agreements, Information and education
Main Content of the Standard
The Policy and Action Standard offers comprehensive guidance across several critical areas. It directs entities on identifying impactful policies and actions for assessing their potential effect on GHG emissions. The standard emphasizes establishing a baseline scenario to compare emissions reductions realistically. Guidance is provided on estimating GHG effects through data collection, emission factors application, and consistent calculation methods. It stresses the importance of transparently monitoring and reporting policy outcomes, tracking progress, and making necessary adjustments. Additionally, recommendations for uncertainty assessment and sensitivity analyses enhance the reliability and accuracy of GHG estimates. This standard is instrumental in supporting entities to enact effective climate policies and actions while ensuring accountability and transparency.
The Product Standard is a vital component of the GHG Protocol that provides guidelines for companies to measure and manage the greenhouse gas emissions associated with individual products throughout their life cycles. This standard is essential for companies aiming to understand and reduce the environmental impact of their products from creation to disposal .
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Product Standard is to help companies comprehensively assess the GHG emissions of their products, enabling them to identify key areas for improvement and enhance sustainability. The scope of the Product Standard covers the entire life cycle of a product, including: Raw material extraction, Manufacturing, Distribution and retail, Use phase, End-of-life.
Main Content of the Standard
The Product Standard provides guidelines for defining product life cycle boundaries for accurate GHG inventory, collecting data using Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) methodologies, and calculating emissions with appropriate factors. Equally important is the guidance on allocating emissions among products, pinpointing emission “hotspots” for strategic mitigation, and promoting transparent reporting practices. This standard empowers businesses to develop impactful strategies for enhancing energy efficiency, optimizing supply chains, and promoting sustainable product use and disposal, thereby bolstering their commitment to environmental stewardship.
The Project Protocol is a key standard within the GHG Protocol, offering guidelines for quantifying and reporting greenhouse gas reductions from specific projects. This standard is essential for organizations looking to implement and validate GHG reduction projects, ensuring that these initiatives contribute effectively to climate goals.
Purposes and Scopes
The primary purpose of the Project Protocol is to provide a standardized approach for assessing the GHG impacts of projects aimed at reducing emissions. This includes projects in various sectors such as energy, agriculture, waste management, and industrial processes.
The scope of the Project Protocol encompasses a broad range of project types, including but not limited to: Renewable energy projects, Energy efficiency projects, Carbon sequestration projects, Waste management projects, Industrial process improvements, …
Main Content of the Standard
The Project Protocol provides guidelines for quantifying and reporting GHG reductions from specific projects. It helps organizations define project boundaries, establish a baseline scenario, and calculate actual GHG reductions. The protocol emphasizes ongoing monitoring, third-party verification, and transparency in reporting to ensure the credibility and effectiveness of GHG reduction projects. Additionally, it includes assessing potential leakage and ensuring comprehensive public disclosure and stakeholder engagement.
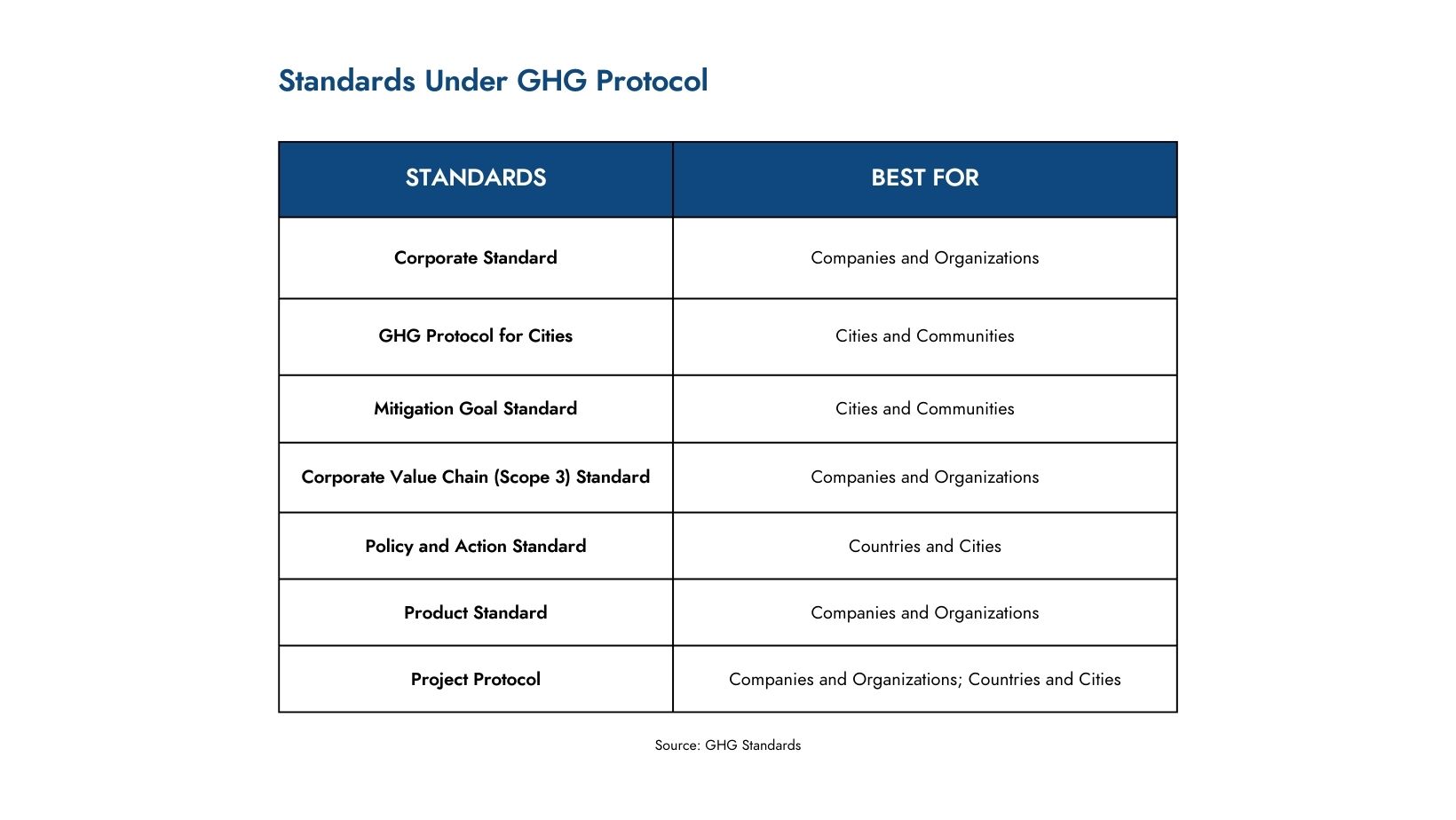
Standards under GHG Protocol
In conclusion, the seven GHG Protocol standards provide comprehensive and detailed guidance for various entities to measure, manage, and reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. From the Corporate Standard’s robust framework for organizational emissions to the specialized standards for cities, products, and value chains, each standard addresses specific needs and challenges. The Policy and Action Standard and the Mitigation Goal Standard guide entities in setting and achieving effective GHG reduction goals, while the Corporate Value Chain (Scope 3) Standard ensures a thorough assessment of indirect emissions. Together, these standards form a critical toolkit for advancing global sustainability efforts and achieving meaningful climate action.
Sources:
https://ghgprotocol.org/standards
https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-standard
https://ghgprotocol.org/ghg-protocol-cities
https://ghgprotocol.org/mitigation-goal-standard
https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-value-chain-scope-3-standard
https://ghgprotocol.org/policy-and-action-standard
Monitor ESG performance in portfolios, create your own ESG frameworks, and make better informed business decisions.
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com7 Straits View, Marina One East Tower, #05-01, Singapore 018936
+(65) 6223 8888
Carrer de la Tapineria, 10
Ciutat Vella, 08002, Barcelona, Spain
+34 612 22 79 06
77 Dunhua South Road, 7F Section 2, Da'an District Taipei City, Taiwan 106414
(+886) 02 2706 2108
Av. Santo Toribio 143,
San Isidro, Lima, Peru, 15073
(+51) 951 722 377