Interested? Contact us now
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), established by the Financial Stability Board, aims to improve and increase the reporting of climate-related financial information. Its significance is underscored by the fact that over 1,500 organizations globally have expressed support for TCFD, highlighting a widespread commitment to transparent and consistent climate-related financial reporting. According to TCFD’s 2021 Status Report, 50% of the world’s top 100 public companies support or report in line with TCFD recommendations, emphasizing the growing importance of these disclosures .
As the effects of climate change become more pronounced, investors and stakeholders are demanding more comprehensive information on how companies are addressing climate-related risks and opportunities. Effective climate-related financial disclosures are crucial for enabling informed investment decisions and fostering a more sustainable economy.
This article aims to explore the four core elements of TCFD reporting—governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets. By understanding these components, organizations can better navigate the complexities of climate-related financial disclosures and enhance their transparency and accountability.
The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) aims to standardize climate-related financial risk disclosures for companies, banks, and investors. Its primary goal is to ensure consistent and transparent reporting on climate risks and opportunities, helping stakeholders make informed decisions. TCFD recommendations focus on four key areas: governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets.
Established in 2015 by the Financial Stability Board (FSB), the TCFD addresses the need for better climate-related financial information . Under Michael Bloomberg’s leadership, the TCFD released its final recommendations in 2017, quickly gaining widespread support and shaping ESG reporting standards.
TCFD reporting provides several key benefits:
Enhanced Transparency: Provides clear and comparable ESG information, aiding stakeholders in understanding climate-related risks and opportunities.
Improved Risk Management: Encourages systematic evaluation and disclosure of climate risks, leading to more resilient business strategies.
Informed Investment Decisions: Offers investors the data needed to incorporate ESG factors into their decision-making processes.
Long-term Financial Performance: Supports sustainable business practices that contribute to long-term economic stability and performance.
By following TCFD recommendations, companies can improve their ESG reporting and better manage climate-related financial risks.
Definition and Key Aspects
Governance refers to the organization’s oversight of climate-related risks and opportunities. It involves the board’s role in assessing and managing these risks and how climate considerations are integrated into the company’s overall governance structure.
Examples
A company might establish a dedicated climate committee within its board to oversee climate-related issues.
Regular board meetings could include reviews of climate-related performance and risk assessments.
Definition and Key Aspects Strategy focuses on the actual and potential impacts of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization’s businesses, strategy, and financial planning. This includes understanding the resilience of the organization’s strategy under different climate scenarios.
Examples
A company might develop a business strategy that includes investments in renewable energy to mitigate transition risks.
Scenario analysis could be used to assess the long-term impacts of climate change on the company’s supply chain.
Definition and Key Aspects Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and managing climate-related risks. It requires integrating these risks into the organization’s overall risk management framework.
Examples
A company might incorporate climate-related risks into its enterprise risk management processes.
Specific measures, such as flood defenses for facilities, could be implemented to mitigate physical risks.
Definition and Key Aspects Metrics and targets are used to assess and manage relevant climate-related risks and opportunities. This includes disclosing the metrics used by the organization to assess climate-related risks and opportunities and the targets set to manage these risks.
Examples
A company might set targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and report progress annually.
Metrics could include energy consumption, carbon footprint, and the percentage of revenue from sustainable products.
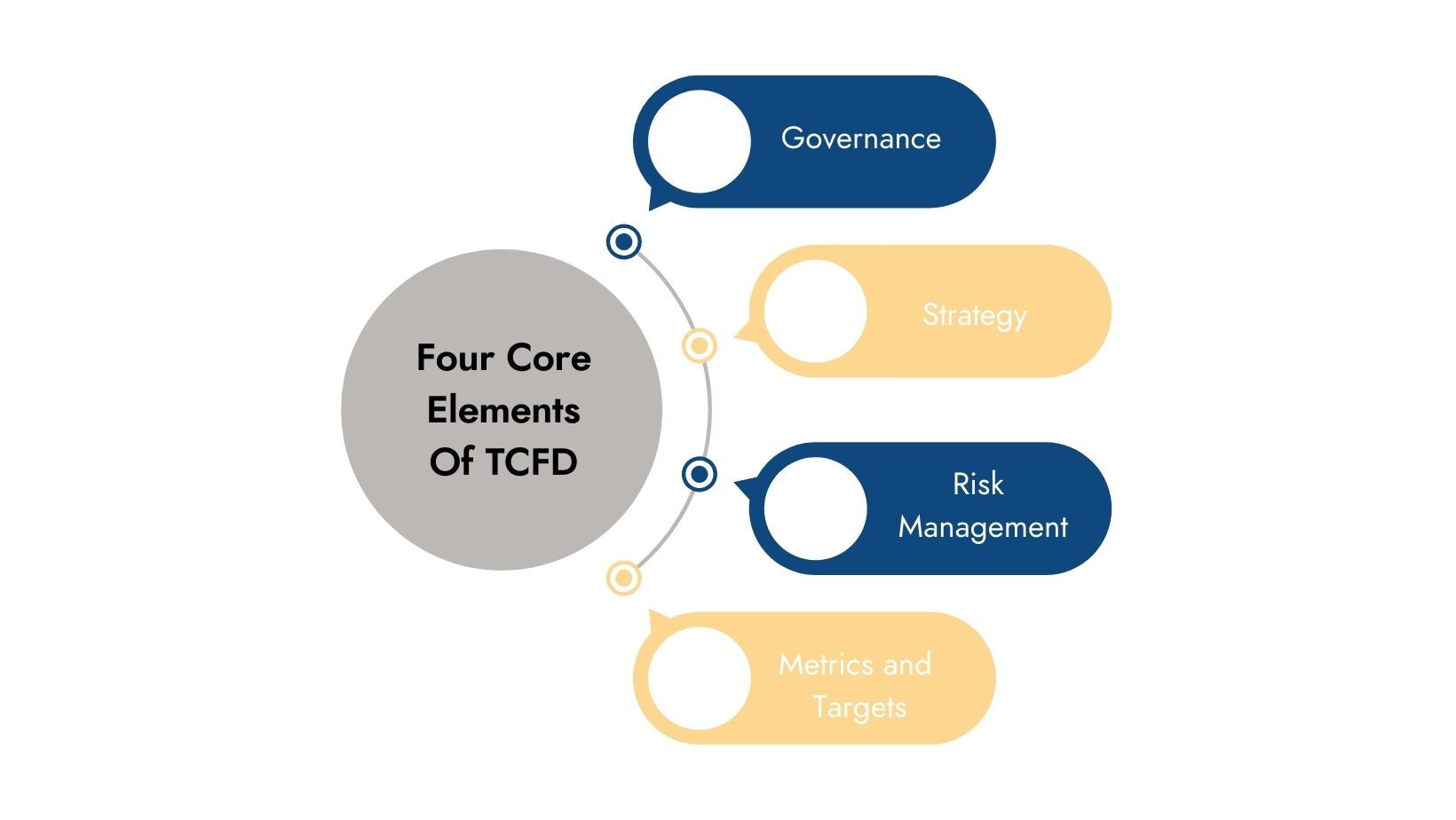
The Four Core Elements of TCFD Disclosure
Data Quality and Availability
Issues Related to the Quality and Availability of Data One of the significant challenges in TCFD reporting is ensuring the quality and availability of relevant data. Companies often struggle with inconsistent or incomplete data, which can hinder accurate climate-related financial disclosures. The complexity of gathering data from various sources and ensuring its reliability adds to the challenge.
Solutions for Improving Data Collection and Analysis
Standardized Data Collection Methods: Implementing standardized methods for data collection can improve consistency and accuracy.
Advanced Analytics: Leveraging advanced analytics and AI technologies can help in better data analysis and insights generation.
Collaboration: Working with industry groups and stakeholders to develop common data standards and sharing practices.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating Different Regulatory Requirements Companies face the challenge of complying with diverse regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. The evolving nature of these regulations adds another layer of complexity, as companies must stay updated with the latest changes and ensure their reporting practices are aligned.
How to Ensure Compliance with Evolving Regulations
Regular Monitoring: Keeping track of regulatory updates and understanding their implications for TCFD reporting.
Integrated Compliance Systems: Using integrated compliance systems that can adapt to new regulations and automate parts of the compliance process.
Expert Consultation: Seeking guidance from experts in regulatory compliance to navigate complex regulatory landscapes effectively.
Resource Allocation
Challenges Related to Allocating Resources for TCFD Reporting Allocating sufficient resources—financial, human, and technological—is a common challenge for companies striving to meet TCFD reporting requirements. Smaller organizations, in particular, may struggle with the financial burden and the need for specialized expertise.
Strategies for Efficient Resource Management
Prioritization: Prioritizing key areas that require immediate attention can help manage resources effectively.
Outsourcing: Collaborating with external consultants or service providers can alleviate some resource constraints.
Training and Development: Investing in employee training to build internal expertise in TCFD reporting and climate-related financial disclosures.
By addressing these challenges through strategic measures, companies can improve their TCFD reporting processes and enhance their overall ESG reporting framework.
As climate-related financial disclosures become more critical, several trends are expected to shape the future of TCFD reporting:
Increased Standardization and Regulation Global efforts to standardize TCFD reporting will ensure consistency and comparability. Enhanced regulatory frameworks will drive companies to adopt comprehensive TCFD-aligned reporting practices.
Technological Advancements AI and big data analytics will streamline data collection and provide deeper insights into climate-related risks. Blockchain technology may enhance transparency and traceability of disclosures, boosting stakeholder trust.
Integration with Financial Reporting TCFD reporting will increasingly integrate with traditional financial reporting. Companies will embed climate-related risks and opportunities into financial statements and strategic planning, using scenario analysis and stress testing to assess resilience under various climate scenarios.
Stakeholder Engagement and Transparency Enhanced engagement with stakeholders will be crucial for effective TCFD reporting. Companies will need to communicate their climate-related strategies clearly, providing detailed and transparent disclosures to meet growing demands for reliable ESG information.
By embracing these trends, companies can improve their TCFD reporting, contributing to a more sustainable global economy and better meeting the needs of investors and other stakeholders.
In an era where climate change poses significant risks and opportunities, effective climate-related financial disclosures are paramount. The TCFD framework provides a comprehensive structure for companies to enhance transparency and accountability in their ESG reporting. By focusing on the four core elements—governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets—organizations can better manage climate-related risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Despite challenges such as data quality, regulatory compliance, and resource allocation, strategic approaches can help overcome these hurdles. As the landscape of TCFD reporting evolves, trends like increased standardization, technological advancements, integration with financial reporting, and enhanced stakeholder engagement will shape its future.
Embracing TCFD recommendations not only supports long-term financial performance but also contributes to a more resilient and sustainable global economy. Companies that proactively adopt and refine their TCFD reporting practices will be better positioned to navigate the complexities of climate-related financial risks and opportunities, ultimately benefiting their stakeholders and the broader community.
Sources:
https://assets.bbhub.io/company/sites/60/2021/07/2021-TCFD-Status_Report.pdf
Monitor ESG performance in portfolios, create your own ESG frameworks, and make better informed business decisions.
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com7 Straits View, Marina One East Tower, #05-01, Singapore 018936
+(65) 6223 8888
Carrer de la Tapineria, 10
Ciutat Vella, 08002, Barcelona, Spain
+34 612 22 79 06
77 Dunhua South Road, 7F Section 2, Da'an District Taipei City, Taiwan 106414
(+886) 02 2706 2108
Av. Santo Toribio 143,
San Isidro, Lima, Peru, 15073
(+51) 951 722 377