Interested? Contact us now
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as crucial metrics for assessing the efficiency and success of an organization’s operations. These quantifiable values enable businesses to measure their progress towards achieving key business objectives. KPIs vary significantly across industries due to differing goals and performance criteria. However, at their core, they provide a clear, objective way of evaluating performance over time. From financial health, such as revenue growth and profit margins, to operational aspects, including customer satisfaction and employee engagement, KPIs encompass a broad spectrum of metrics. Their primary utility lies in their ability to give stakeholders a comprehensive snapshot of an organization’s health and guide strategic decision-making.
ESG Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) refer specifically to metrics used to assess an organization’s performance in terms of environmental, social, and governance factors. These indicators provide a framework for evaluating how a company’s operational processes align with sustainable and ethical principles. By focusing on the ESG criteria, businesses can monitor their impact on the environment, their relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the community, as well as their governance standards.
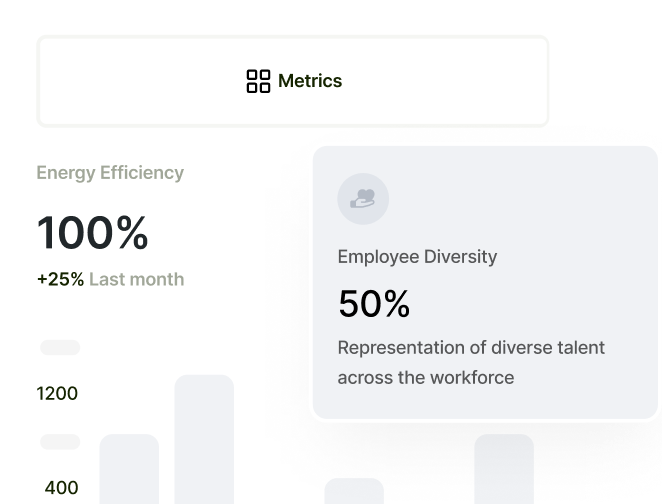
Environmental KPIs might include metrics like carbon footprint, energy efficiency, waste management, and water usage, assessing how a company’s operations affect the natural world. Social KPIs, on the other hand, focus on the company’s impact on people and society, measuring factors such as employee diversity and inclusion, labor standards, community engagement, and customer satisfaction. Governance KPIs evaluate the company’s leadership, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights, ensuring accountability and transparency in its operations.
Tracking these ESG KPIs allows companies not only to comply with regulatory requirements and meet investor expectations but also to identify risks and opportunities for improvement within their operations. By integrating ESG factors into their performance metrics, businesses can achieve a more sustainable and ethical approach to their operations, which can contribute to long-term profitability and stakeholder trust.
ESG KPIs are based on a variety of standards and frameworks that provide guidelines for businesses on how to measure and report their impact in terms of environmental, social, and governance aspects. These standards help ensure that reporting is consistent, comparable, and transparent across different organizations and sectors. Some of the most widely recognized standards include the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) [1].
The adoption of these standards by businesses in their ESG reporting enhances the credibility of the reported information, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and compare companies’ performance on ESG criteria. This, in turn, facilitates better decision-making by investors, regulators, and other stakeholders looking to assess a company’s commitment to sustainable and ethical principles.
The realm of ESG Key Performance Indicators is vast and varied, reflecting the broad spectrum of environmental, social, and governance areas businesses need to monitor. Although the specifics can vary widely by industry and corporate strategy, here is a concise overview of common ESG KPI examples, grouped by category, to illustrate the kinds of metrics companies might track.
Environmental KPIs Examples
Social KPIs Examples
Governance KPIs Examples
Setting effective ESG KPIs requires a strategic approach that aligns with both the overarching goals of the organization and sustainability objectives. Initially, companies should conduct a comprehensive materiality assessment to pinpoint the ESG issues that are most relevant to their business operations and stakeholder interests. This assessment will help prioritize focus areas and ensure that the selected KPIs are meaningful and impactful. Engaging with stakeholders – including investors, customers, and employees – during this process can provide valuable insights into the expectations and concerns that could shape your ESG agenda.
Once the key areas of focus have been identified, companies should establish clear, actionable KPIs that are both measurable and time bound. This involves setting specific targets which can vary from reducing greenhouse gas emissions to enhancing diversity within the workforce. The KPIs should be integrated into the broader business strategy, ensuring they are not siloed but rather contribute to the overall success and sustainability of the business. Furthermore, leveraging recognized ESG reporting frameworks and standards can help in setting credible and consistent KPIs that are aligned with best practices and can be benchmarked against industry peers.
Lastly, transparency and continuous improvement are critical components of successful ESG KPI implementation. Companies should regularly monitor, report, and communicate their progress towards these sustainability goals. This includes being open about the challenges faced and the lessons learned. By doing so, businesses not only demonstrate their commitment to sustainability but also build trust with their stakeholders. It is also important to review and adjust KPIs as necessary to reflect changing regulations, market conditions, or strategic priorities, ensuring that the ESG efforts remain relevant and ambitious over time.
The future of ESG KPIs is poised to evolve dramatically as regulatory pressures increase and societal expectations shift towards greater accountability and transparency in corporate environmental, social, and governance practices. This evolution will likely see a significant enhancement in the sophistication and granularity of ESG metrics, driven by advancements in technology and data analytics.
Furthermore, increased harmonization of global ESG reporting standards will enable more consistent and comparable ESG disclosures, facilitating better scrutiny and decision-making by investors, consumers, and other key stakeholders. As awareness and concern about sustainability issues grow, companies that proactively engage with and report on ESG factors will not only mitigate risks but also seize new opportunities for innovation and competitive advantage.
In this dynamic landscape, the integration of ESG KPIs into digital reporting platforms using blockchain or AI technologies could serve as a game-changer, ensuring real-time, tamper-proof reporting and enhancing stakeholder confidence in the reliability of disclosed information. Likewise, as the focus on impact investing intensifies, the demand for more outcome-based KPIs will rise, pushing companies to demonstrate not just efforts in sustainability but actual positive outcomes for society and the environment. The role of ESG KPIs is thus expected to shift from mere performance indicators to becoming critical tools in shaping business strategies, driving sustainable practices, and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability in the corporate sphere.
References:
Monitor ESG performance in portfolios, create your own ESG frameworks, and make better informed business decisions.
In order to contact us please fill the form on the right or directly email us at the address below
sales@senecaesg.com7 Straits View, Marina One East Tower, #05-01, Singapore 018936
+(65) 6223 8888
Gustav Mahlerplein 2 Amsterdam, Netherlands 1082 MA
(+31) 6 4817 3634
77 Dunhua South Road, 7F Section 2, Da'an District Taipei City, Taiwan 106414
(+886) 02 2706 2108
Viet Tower 1, Thai Ha, Dong Da Hanoi, Vietnam 100000
(+84) 936 075 490
Av. Santo Toribio 143,
San Isidro, Lima, Peru, 15073
(+51) 951 722 377
1-4-20 Nishikicho, Tachikawa City, Tokyo 190-0022